The Indus Waters Treaty (1960): Overview and Impact
The Indus Waters Treaty (1960): Overview and Impact
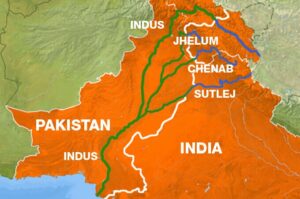
The Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) is a landmark water-sharing agreement signed on September 19, 1960, between India and Pakistan, with the World Bank acting as a broker. It governs the use of the waters of the Indus River system, which includes six rivers: Indus, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej.
Key Provisions
The treaty divides the river system between the two nations:
Western Rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab): Allocated to Pakistan.
Eastern Rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej): Allocated to India.
India is permitted limited use of the western rivers for:
Domestic use
Non-consumptive use (e.g., navigation, fisheries)
Agricultural use (within limits)
Hydroelectric power generation (without storage or altering flow)
Significance and Impact
Regional Stability
The IWT has survived multiple wars and political crises between India and Pakistan, acting as a rare example of cooperation and communication.
It established a Permanent Indus Commission, facilitating annual meetings and data sharing.
Water Security
The treaty provides Pakistan with rights over 80% of the river waters, which are vital for its agriculture-based economy.
India retains control over 20% but faces constraints on usage of western rivers, especially for hydro projects.
Disputes and Challenges
India’s hydroelectric projects (like Baglihar and Kishanganga) have led to disputes, with Pakistan raising objections over treaty violations.
The World Bank has intervened in some cases, but resolution mechanisms remain slow.
Climate Change and Population Pressure
Growing demand, reduced glacier flow, and unpredictable monsoons have increased tension over water scarcity.
Both countries face pressure to modernize irrigation and storage systems without breaching treaty terms.
Strategic and Political Leverage
India has occasionally discussed reviewing or revoking the treaty as a form of pressure during diplomatic conflicts.
However, such moves are constrained by international law and treaty obligations.
Conclusion
The Indus Waters Treaty is considered one of the most successful international water-sharing agreements. Despite persistent tensions and evolving environmental challenges, it continues to play a crucial role in maintaining a fragile peace over a vital shared resource between India and Pakistan.
Do charity
#BanoKisiKiMuskan
Be someone’s reason to smile
For Donation call us @ 9711364750
www.padindia.org
Send ur resume at
info@padindia.org
https://www.youtube.com/padindia
https://www.linkedin.com/company/padindia
https://www.facebook.com/Padvoice/
https://www.facebook.com/voiceofindiantaxpayers/